What are the 7 Regions of China?
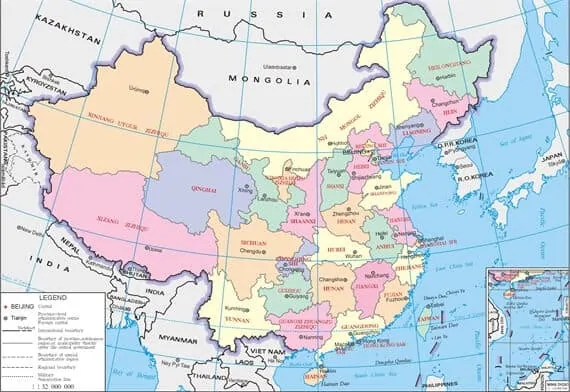
Northeast China
A Region with Early Economic Start in the 7 Regions of China
Northeast China refers to Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning, as well as four cities of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. In addition, Northeast China, with four distinct seasons, is a region with rich resources, prosperous culture, and strong economic strength. And so this region plays an important role in the country.
The economy of Northeast China started much earlier than others. So it made a great contribution to the development of new China, strongly supporting the national economic construction. What’s more, the fertile black land is responsible for the agricultural development of Heilongjiang and Jilin being largely agricultural. As a result, this region is rich in rice, corn, soybeans, potatoes, beets, sorghum, fruits, and vegetables.
North China
The Political and Cultural Center in the 7 Regions of China
North China includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and the central part of Inner Mongolia (Hohhot, Chifeng, Baotou, Erdos, and Ulanchab). Its total area is 838100 square kilometers, accounting for 8.7% of China’s total area. The soil in North China is the Yellow River alluvial type, which is good for, and thereby makes this province the main wheat-producing area in China.
North China is one of the birthplaces of the Chinese nation and the political and cultural center of China. Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is the largest and most dynamic economic area in northern China.
Central China
The Transportation Center of China in the 7 Regions of China
Central China includes Henan, Hubei, and Hunan, which covers an area of 560000 square kilometers, accounting for 5.9% of the country’s total land area. By the end of 2017, the permanent population of central China was about 223 million, with a GDP of about 11.61 trillion yuan and a per capita GDP of about 52000 yuan.
Central China, with its rich history and culture, developed agriculture, rich mineral resources, a solid foundation of light and heavy industries, and convenient land and water transportation. It is a relatively developed region in China’s economy and the transportation center of China.
East China
The Most Developed Areas in the 7 Regions of China
East China includes Shandong, Jiangsu, Anhui, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Taiwan. The total area is 834300 square kilometers, accounting for 8.7% of China’s landmass.
East China is the economic zone with the highest comprehensive technical level in China, with a superior natural environment, abundant natural resources, developed commodity production, and complete industrial categories. The light, machinery and electronic industries occupy the leading position in China. Railway, water transport, highway and shipping all fall under one umbrella, and are the most developed areas of China’s economy and culture.
Southwest China
The Important Development Areas in the 7 Regions of China
The terrain structure of Southwest China is complex, consisting of mainly plateau and mountain areas, with a total area of 2.351 million square kilometers. It includes Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Tibet Autonomous Region.
Southwest China is an important base for the development and strategic reserve of China’s nonferrous metals industry and so one of the important development areas in the 21st century. In addition, Sichuan Province and Chongqing are the areas with the densest population. As a result, they are the most convenient and the most developed economies in this region.
Northwest China
The Regions Deep Inland
The northwest region includes Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Its total area is 3.080008 million square kilometers. Some of the main cities are Xi’an, Lanzhou, Xining, Yinchuan, and Urumqi.
Because the northwest region is deep inland and far away from the sea, with the high plateau and mountainous terrain blocking the humid airflow, the precipitation in this region is rare. In addition, there are more sandstorms, and the ecology is fragile. What’s more, the area is sparsely populated, rich in resources and difficult to develop. However, the region has a long international border, which is conducive to border trade.
South China
The Leader in Economic and Social Development.
China regards Fujian, Guangdong, and Hainan as key home towns of overseas Chinese, because South China includes Guangdong, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macao Special Administrative Region, Hainan, and adjacent islands such as Zhongsha Islands, Nansha Islands, Xisha Islands, Dongsha Islands, Diaoyu Islands, and their affiliated Islands, Bailongwei Island and so on. Although Fujian and Taiwan belong to East China, they are more similar to South China in terms of culture, customs, blood relations, and personnel movement. As a result, some people may regard them as areas belonging to South China.
South China, by virtue of its geographical advantages adjacent to Hong Kong, Macao, and Southeast Asia, is the leader in economic and social development.



