What do you know about China’s ID card?
China’s ID card, also known as the Resident Identity Card, is the same size as an ordinary credit card. If you trade with Chinese companies, you are likely to see or use the original or scanned copy of China’s ID card of the employees of those companies.
According to the regulations, Chinese citizens who have reached the age of 16 must apply for a resident identity card. However, citizens who have not reached the age of 16 may also apply for a resident identity card in accordance with the regulations. This ID card contains a lot of information: name, gender, nationality, date of birth, address, ID number, etc. The emergence of a large number of new technologies allows identity cards to contain a variety of biometric information, such as photos, facial features, palm features.
Many Chinese always carry their ID cards with them. An ID card is used on many occasions, such as household registration, employment, notarization, exit application, litigation, individual business license, personal credit, and other financial business, hotel registration and so on.
China’s ID Card’s details
On April 6, 1984, the State Council of the People’s Republic of China issued the first generation of resident identity cards. From March 29, 2004, mainland China officially began to issue the second generation of ID cards for residents. The second generation of ID cards has a built-in contactless IC card smart chip. Its surface adopts anti-counterfeiting film and printing anti-counterfeiting technology, and the information in the digital chip can be read by a machine.
With the introduction of the ID card, the government made it a requirement for all persons 16 years and older to apply for an ID card. Though not a must, anyone under the age of 16 also has the ability to acquire one.
Here is a pattern on the front of the ID card.
The front of the ID card includes the following information:
- The national emblem
- Certificate name, i.e. “People’s Republic of China Resident Identity Card”
- Issuing authority, i.e. the name of the district/County Public Security Bureau issuing the ID card
- Period of Validity (under 16 years old: five years; 16-25 years old: ten years; 26-45 years old: twenty years; over 46 years old: long term)
Here is a pattern on the reverse of the ID card.
The reverse side of the ID card includes the following information:
- Name
- Gender
- Ethnicity
- Date of birth
- Address: (the address of the holder’s residence, but not necessarily the current address of the holder)
- Citizen Identity Number
What is China’s ID Card Citizen Identity Number?
The citizenship number is 18 digits in total, which is composed of a 17 digit body code and one check code. The sequence from left to right is a six-digit address code, an eight-digit birthdate code, a three-digit sequence code, and a one-digit verification code.
1. Address code
Indicates the administrative division code of the county (county-level city, flag, district) where the holder’s permanent residence is located. The coding rules are:
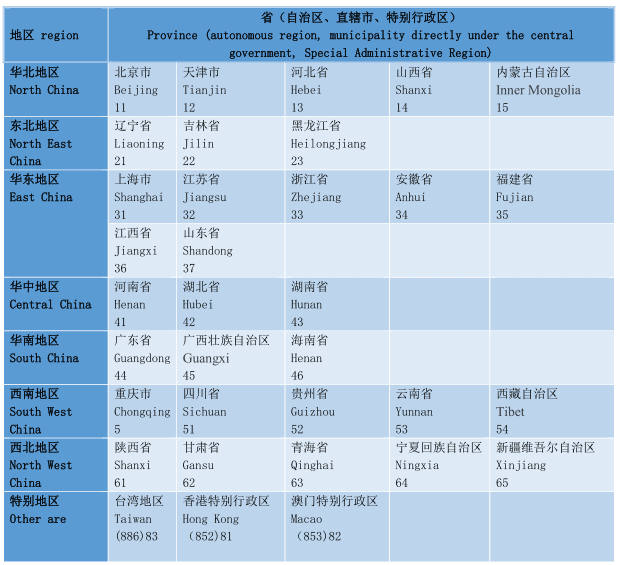
The first and second digits represent provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the central government, and special administrative regions).
The third and fourth digits indicate the city (the summary code of the municipal districts and counties of prefecture-level cities, autonomous prefectures, leagues, and municipalities directly under the central government). Among them, 01-20, 51-70 represent provinces and municipalities directly under the central government; 21-50 represent regions (autonomous prefectures and leagues).
The fifth and sixth digits represent counties (municipal districts, county-level cities, and flags). 01-18 refers to the county-level city under the jurisdiction of municipal district or region (autonomous prefecture, League); 21-80 refers to the county (flag); 81-99 refers to the county-level city directly under the provincial government.
2. Date of birth code
The seventh to fourteenth digits of ID card number indicates the year, month and day of the birth of the holder, among which the year is represented by four digits, and there is no separator between the year, month and day. For example, May 11, 1981, is represented by 19810511.
3. Order code
The sequence code is the 15th to 17th digits of the ID card number. It is the sequence number of persons born in the same year, month and day within the area marked by the address code. Seventeen of them were given odd numbers to men and even numbers to women.
4. Checksum
The check code as the tail number is calculated according to the first 17 digits. In addition, if someone’s suffix is 0-9, there will be no X, but if the suffix is 10, use the Roman numeral X instead.
Our Other Introductions
How to judge whether your suppliers are reliable?
What are the 7 Regions of China?
The Top 10 China Sourcing Websites